Introduction
Adenoidid is a condition that often develops quietly but can strongly affect breathing, sleep quality, speech, and overall well-being—especially in children. Many parents and adults overlook early signs, assuming they are minor colds or seasonal allergies. However, when left unmanaged, this condition can interfere with daily life and long-term health.
This in-depth guide explains everything you need to know, from how the condition develops to modern treatment options. The goal is to help readers make confident, informed decisions using clear language, practical examples, and medically accurate insights.
What Is Adenoidid?
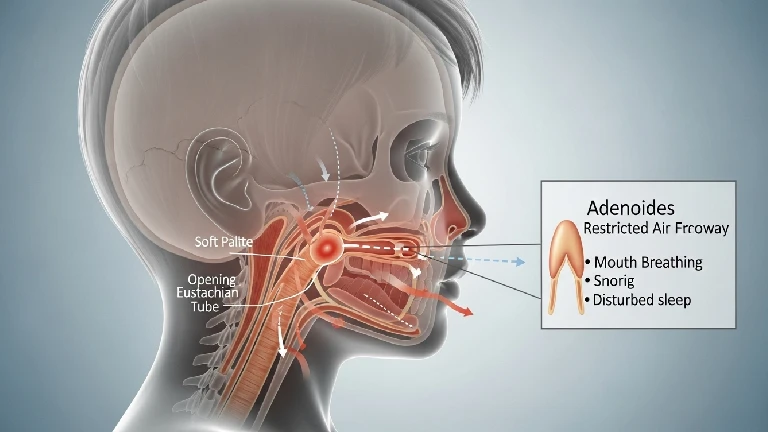
Adenoids are small masses of immune tissue located behind the nose, above the throat. They play an important role in early childhood by trapping germs entering through the nose. When these tissues become inflamed or infected repeatedly, adenoidid develops.
This inflammation may be temporary or persistent. In chronic cases, the swollen tissue blocks airflow, leading to breathing difficulties, nasal speech, and recurring infections. While most common in children, adults can also experience symptoms under certain conditions.
Main Causes of Adenoid Inflammation
Several factors contribute to adenoid enlargement and infection. Understanding these causes helps reduce recurrence and supports effective treatment.
Frequent Infections
Repeated exposure to viruses and bacteria strains the immune system, causing the adenoids to remain enlarged instead of shrinking naturally.
Allergic Reactions
Long-term allergies cause ongoing nasal irritation, increasing inflammation and mucus production.
Environmental Triggers
Exposure to smoke, air pollution, or poor indoor air quality can worsen symptoms and delay recovery.
Weakened Immune Response
Children with developing immune systems or adults with immune stress face a higher risk.
Xmegle Explained: Discover a Smarter Way to Connect Instantly Online
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Symptoms vary by age and severity but often worsen gradually.
-
Constant nasal congestion
-
Mouth breathing, especially during sleep
-
Loud snoring or sleep disturbances
-
Nasal or muffled voice
-
Recurrent ear infections
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Daytime fatigue due to poor sleep
Recognizing these early signs allows faster medical intervention and reduces complications.
How the Condition Is Diagnosed
Doctors typically use a combination of physical examination and symptom history. In some cases, imaging or a small camera examination through the nose helps assess the size and severity of the inflamed tissue.
Diagnosis focuses on ruling out similar conditions while confirming persistent inflammation that interferes with breathing or hearing.
Treatment Options Explained Simply
Treatment depends on age, severity, and response to earlier care. Mild cases often respond well to non-surgical approaches.
Medical Management
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
-
Allergy control plans
-
Nasal sprays to reduce swelling
-
Antibiotics when bacterial infection is present
Surgical Intervention
When symptoms persist or worsen, doctors may recommend removal of the adenoids. Surgery is typically safe, fast, and effective, especially in children with chronic breathing or ear issues caused by adenoidid.
Comparison Chart: Treatment Options at a Glance
| Treatment Type | Best For | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medication | Mild cases | Non-invasive, easy | Temporary relief |
| Allergy Control | Allergy-related cases | Reduces recurrence | Requires consistency |
| Watchful Waiting | Minor symptoms | Avoids intervention | Risk of progression |
| Surgery | Chronic cases | Long-term solution | Requires recovery time |
This comparison helps readers weigh benefits against potential limitations before choosing a care path.
Possible Complications If Ignored
Untreated inflammation may lead to long-term problems such as hearing loss, dental alignment issues, facial growth changes in children, and chronic sleep disruption. Early care reduces these risks significantly.
Prevention and Daily Care Tips
-
Maintain good nasal hygiene
-
Reduce exposure to allergens and smoke
-
Treat colds promptly
-
Strengthen immunity through balanced nutrition
-
Ensure clean indoor air
Preventive care plays a key role in reducing flare-ups and improving recovery time.
When to See a Doctor
Medical advice is essential when symptoms persist longer than two weeks, worsen over time, or interfere with sleep, hearing, or daily activities. Early evaluation prevents unnecessary complications.
FAQs
1. Can adenoidid go away on its own?
In mild cases, symptoms may improve as infections resolve or as children grow older. Persistent cases usually need medical care.
2. Is surgery always necessary?
No. Many cases respond well to medication and lifestyle changes. Surgery is considered when symptoms remain severe.
3. Does this condition affect adults?
Yes, although it is less common, adults can develop symptoms due to allergies or repeated infections.
4. How long does recovery take after treatment?
Medication relief can occur within days, while surgical recovery typically takes one to two weeks.
5. Can it come back after treatment?
Recurrence is rare after surgery but possible if underlying allergies or infections continue.
Conclusion
Adenoidid may begin as a minor issue, but its impact can grow if ignored. Understanding symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers individuals and parents to act early. With proper care, most people experience full relief and improved quality of life.
Awareness, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment remain the strongest tools for managing this condition effectively and confidently.